Butterfly numbers
are dwindling amid emergency efforts to mitigate habitat damage by
glyphosate-tolerant crop cultivation
Dr. Eva Sirinathsinghji
Sign the Independent Scientists
Manifesto on Glyphosate here:
https://www.i-sis.org.uk/Independent_Scientists_Manifesto_on_Glyphosate.php
The Monarch butterfly is famed for its spectacular 3 000 mile winter migration from N. America to Mexico before returning to breed in the spring. The journeys of these striking orange, black and white insects span the North American continent, completed by four generations, each interlinking like a relay team to reach their final destination back in N. America. Their migration has been described as one of the world’s most spectacular natural phenomena but over the last few years, fewer and fewer have been observed completing the journey, sparking concern over the future of the species.
It has been suggested that loss of habitat of both its overwintering grounds and breeding grounds as well as severe weather conditions are all contributing to the astonishing decline that has prompted calls for the species to be placed on the endangered species list [1], forcing governments to take action to reverse the trend (see later). Many of these measures however, have been criticised for not tackling the most evident cause of their decline – the destruction of their breeding grounds by widespread glyphosate-use in America’s GM crop farms. Habitat destruction of the wintering grounds in Mexico through illegal logging have also been proposed to have contributed but as explained below, if we are to protect this majestic species, we must address the industrialised GM-crop system that is not only a threat to butterflies, but other pollinators, let alone the health of people.
Long-term studies recently reveal a worrying decline in numbers reaching Mexico since records began in the 1990s [2]. Prior to that, they were described in various publications to be abundant since the 1800s. A research team led by Isabel Ramirez at Universidad Nacional Autonoma in Mexico analysed the total area occupied by the butterflies in hibernation over 17 years (1994-2011) (published online by World Wildlife Fund-Mexico since 1994) using two different statistical methods, and both showed significant decreases [3] (see [4] Glyphosate and Monarch Butterfly Decline, SiS 52). Although the numbers vary from year to year, the highest area reported was in 1997, where they occupied 20.97 ha (hectares). In 2010, the lowest area was recorded, at just 1.92 ha. The 2010-11 season showed a slight increase to 4.02 ha. Since the publication of this study, the numbers dropped lower, with 2013-2014 seeing the worst numbers recorded in Mexico at just 0.67 ha (again performed by the WWF of Mexico and the National Commission of Natural Protected Areas (CONANP) from the Secretariat of Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT)). The results of the study are presented in Figure 1 and have been extended to include more recent surveys as published by the Centre for Food Safety [5]. The year 2015 saw an increase in numbers by 69 %, though we are yet so see if that is a natural fluctuation in the downwards trend or the beginning of a recovery. Yearly fluctuations are common which is why trends over decades offer more insight into the status of the species.
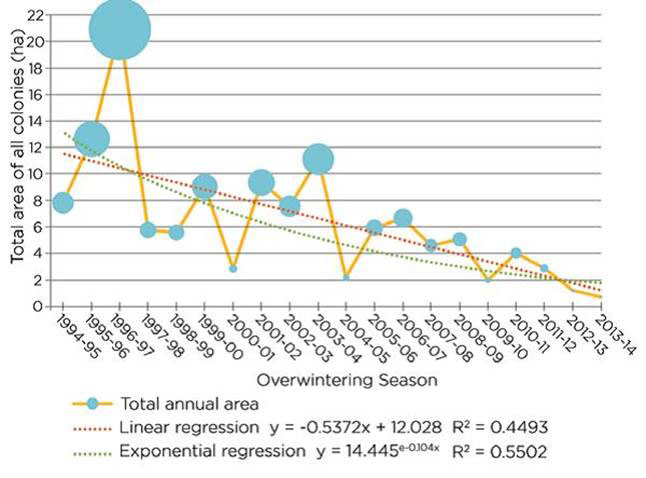
Figure 1 Decline of monarch butterfly over time. Bars represent the total size of colonies over 20 seasons from 1994-5 to 2013-14.
When analysing numbers in N. America, studies have provided some conflicting data on numbers in their breeding grounds and the numbers migrating, though there is little discussion over the fact that numbers reaching Mexico are dwindling.
Analyses of egg density found a reduction from 2006 onwards [6]. Some studies have reported no major downwards trend [7, 8]. This has been suggested to have arisen due to the difficulty in counting the summer and autumn numbers as they breed and migrate across the continent. Using volunteers to collect data as was done in these studies could also have resulted in under-sampling of agricultural areas where herbicides are highly used, with volunteers instead favouring areas where butterflies are common such as parks and wildlife centres. Migration numbers from Ontario, Canada [9] and the Northern part of the US, Michigan [10] also do not show steep declines, suggesting that regions further south are responsible. The migration process may also be affected by weather conditions and the loss of nectar food sources such as wildflowers that the adults feed on though evidence for this is currently lacking. Their complex migratory patterns make them especially vulnerable to an unknown number of threats at different staging posts of their migratory routes often separated by large geographical distances.
Milkweed habitats have been declining since the introduction of GM crops engineered to tolerate glyphosate herbicides in 1996. Though glyphosate was used prior to their introduction, it was limited to pre-emergent application (before crops have started to emerge from the ground) and most milkweed escaped glyphosate exposure. Indeed, there are very few herbicides effective against milkweed, with glyphosate the most effective of all. Furthermore, milkweed is generally considered a low-impact weed with regards to crop loss, making their destruction and that of the monarch totally needless.
Since 1996, thorough weed surveys published in the scientific literature have documented dramatic drops in numbers, particularly in the Corn Belt, including an estimated 50 % reduction in milkweed density in Iowa from 1999 to 2009 [11, 12]. In other US states including Minnesota, a several survey estimated a 100-fold higher level milkweed plants per ha in 2001 compared to 2003-2005 [13]. Out of 453 fields surveyed, milkweed was detected on only 3.4 % of the fields. It is expected that similar patterns of milkweed loss have occurred in other non-surveyed areas in the Midwest where GM soy and corn production is widespread and steadily growing since. Figure 3 shows the increasing glyphosate use as well as the regions, with the Midwest showing some of the highest levels of glyphosate spraying, coinciding with the plantation of GM crops. An in-depth report form the Centre for Food Safety also lists personal observations from farmers that claim farmers have not seen milkweed in their fields for years in regions such as Nebraska and Kansas [5].
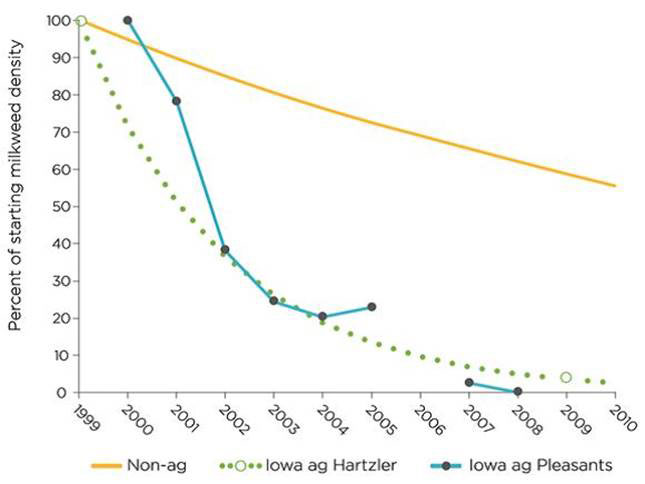
Figure 2 Declines in milkweed density in Iowa
Compilation of two studies surveying milkweed densities by Hartzler [11] and Pleasants [14] in agricultural fields (blue and green) and non-agricultural fields (yellow)
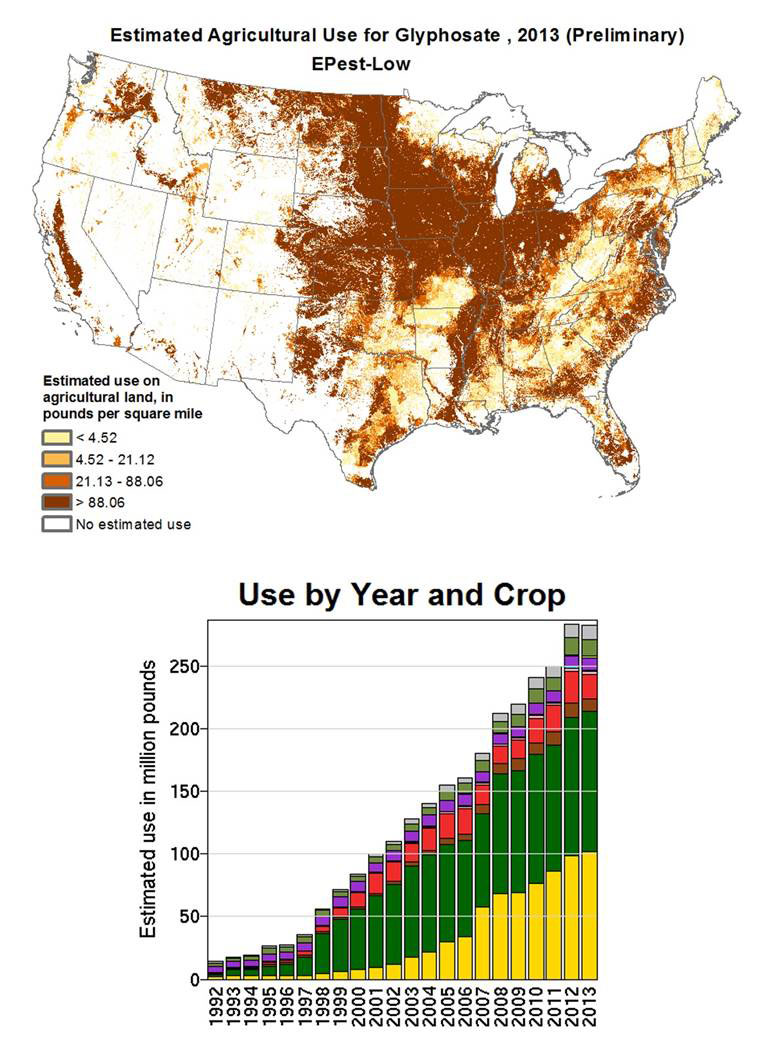
Figure 3 Estimated Glyphosate use in US across nation and per crop species
Glyphosate use has steadily increased in recent years correlating with the planting of glyphosate-tolerant corn and soybeans [15]
It must also be noted that analysis of overwintering butterflies during the 1996-1997 season showed that 50 % of butterflies originate in the Corn Belt, as determined by hydrogen and carbon isotope profiles in the wings which correlates with the latitudes of host plants, allowing researchers to map natal origins. Repeating this work on the 2010/2011 season found that a smaller number of butterflies came from this region, suggesting changes in the heart of the Corn Belt are responsible for lower numbers reaching Mexico [16].
It is clear that monarch numbers are affected by the relative abundance of their only larval food source, but to what extent this is the overriding factor is still argued by those aiming to protect the commercial business of GM crop and pesticide sales. Evidence linking monarch numbers to milkweed decline include an important study that aimed to assess which life-stage, season and geographical region across the annual cycle were contributing most to the declines of overwintering. Using population modelling techniques they compared the three main factors, habitat loss in N. America, habitat loss in Mexico and extreme weather events to see which of these issues were more influential [17]. They found that monarch abundance was more than four times more sensitive to perturbations of vital rates (how fast vital statistics change in a population) on the breeding grounds than on wintering grounds. Simulations that considered only forest loss or climate change predicted higher population sizes compared to milkweed declines, with females unable to lay a full complement of eggs as well as through intraspecific larval competition. The researchers concluded that in order to conserve the species, milkweed habitat conservation is a key though smaller scale efforts such as the planting of milkweed in gardens and roadsides are likely insufficient to negate the loss due to the industrial agricultural practices over the past 2 decades.
Another study on egg numbers in N. America found a direct correlation between the number of eggs laid and the area of glyphosate-tolerant crops planted [6]. The researchers found that they were able to predict the size of the overwintering population in Mexico by egg density and habitat loss of milkweed caused by adoption of glyphosate-tolerant crops. Further, they found declines in egg densities after 2006. This finding suggests that females are not compensating for the loss of host plants in the matrix. The fact that the egg densities are declining after 2006 suggests that the population has reached a point that some of these remaining sites are being found by fewer or no females as the overall population declines.
Attempts are being made to combat the drastic monarch decline. The Mexican government for example, has manged to stem illegal logging of the forests in which the monarchs spend their winters. An estimated 731 ha of land was damaged due to illegal logging from 2005-2007 alone [18]. Efforts have been made to support local people and businesses with employment opportunities to reduce logging for firewood. It has been reported that since November 2015, the Mexican Environmental Protection Office implemented measures that have seen no illegal logging over the last couple of months. Measures have included systematic security tours within the Monarch butterfly Biosphere reserve and the creation of buffer zones to surround conservation areas. However, as reported above, complete protection of overwintering habitats the monarch decline would not be effective if efforts are not made to protect and expand their breeding grounds. In the US, pressure to protect the famous butterfly have spurned new programmes to increase milkweed abundance including a multimillion dollar project by the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), providing financial and technical assistance to help producers plant milkweed and nectar-rich plants along field borders and assist management practices on pastures. However, it is uncertain how this will mitigate the losses caused by glyphosate-spraying [19] which must be addressed for the monarch to flourish once again.
The case for banning glyphosate is overwhelming, and is supported by many independent scientists as evidenced by ISIS’s independent Scientists Manifesto that has attracted hundreds of signatures from scientists as well as non-scientists. As summarised in our recent ISIS special report [21] Banishing Glyphosate, glyphosate exerts multiple modes of toxicity and is a serious threat to the health of people and planet.
Article first published 10/02/16
Comments are now closed for this article
There are 3 comments on this article.
ward johnson Comment left 11th February 2016 19:07:01
In 2014, my wife and I started the SaveOurMonarchs Foundation. You can get Free Milkweed Seeds at SaveOurMonarchs.org
We sent over 1 Million Milkweed Seed Packets in 2015.
We expect to send over 2 Million in 2016.
We would appreciate your support.
Jan Lelie Comment left 26th February 2016 23:11:25
A few weeks ago, my wife and I visited one of the reserves in Mexico. The experience of the migrating butterflies is overwhelming. We'll never forget the sound of their wings.
One of the guides also mentioned the decrease in population over the years, as did somebody who has lived there for over 30 years. It was also attributed to the loss of milkweed in Mexico and the US. Also, they said, there are some reforestation efforts in Mexico. But it might be too late and too little.
Betty Aridjis Comment left 22nd September 2016 23:11:47
Read this very important article about threats facing the monarchs now.
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/homero-aridjis/endangered-monarchs-mexico_b_9832806.html